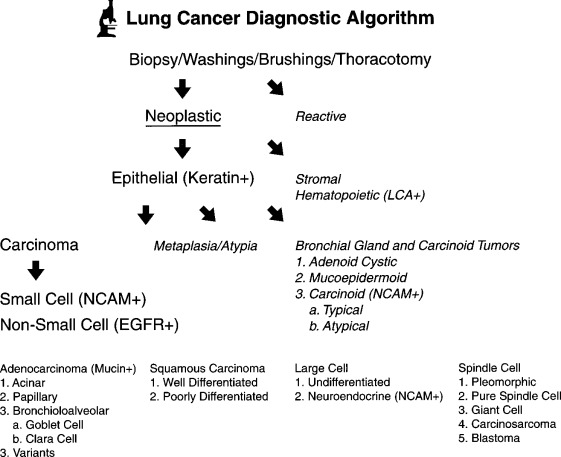
A diagnosis of lung cancer is not easy to make as many symptoms can be caused by other ailments. However, your healthcare provider can make a diagnosis by examining you and reviewing your health history, risk factors, and family medical history. During a physical exam, your healthcare provider may also perform a series of tests to detect lung cancer. A biopsy is the only way to confirm a lung cancer diagnosis. A small sample of tissue is taken from the tumor and tested for cancer cells. Other tests can determine the stage of the disease, including imaging studies and PET scans.
Other types of tests may be performed during a lung cancer diagnosis. For example, if a family member had lung tumours when he was a child, this gene increases your risk of developing the disease. The type of tests your healthcare provider recommends depends on the stage of the disease. If you’re diagnosed with lung cancer, a CT scan can help your doctor decide the best treatment options for you. While you may be concerned about the cost of these tests, these treatments are often very effective for most patients.
Early diagnosis of lung cancer can be treated through surgery, and radiotherapy can be used to kill cancerous cells. If the disease is advanced, a doctor may recommend chemotherapy. Targeted therapies are drugs that target specific changes in cancer cells and may help slow its growth. Some of these drugs also inhibit the growth of the tumors. In addition, targeted therapies may be used to treat lung cancer that has already spread. A healthcare professional should use the latest treatment options to ensure that your recovery is successful.
Early diagnosis of lung cancer can be achieved through surgery or radiotherapy, which removes the cancerous cells. More advanced stages of the disease may require chemotherapy or radiation therapy. When these therapies fail to work, treatment with targeted therapies is an option. These medications are intended to stop the spread of the cancer. Once you’ve been diagnosed, you’ll be on the road to recovery. So, the sooner you start your treatment, the better.
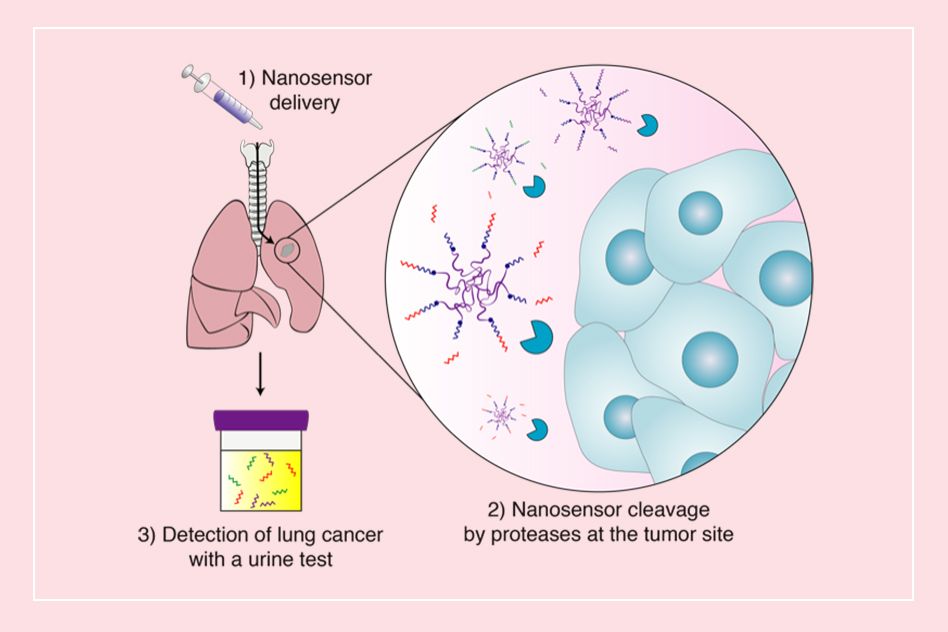
After an initial diagnosis of lung cancer, you’ll need to undergo additional tests to learn more about your condition. You will be given a full diagnosis. During your treatment, you’ll receive an examination. A chest X-ray or CT scan will determine your exact diagnosis. If your disease is still localized, a biopsy will allow your healthcare provider to decide on the best treatment options. If it has spread, it may be treated with chemotherapy.
The treatment for lung cancer depends on the stage of the disease. In cases of early stage disease, surgery and radiotherapy are used to destroy the tumor. If it has spread to other parts of the body, you’ll need chemotherapy for advanced stage lung cancer. It is not easy to decide which treatment is best for your condition. Depending on your situation, you may need a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. You may even need surgery. The best lung cancer treatment for you will depend on where you live and the type of the disease.
After a lung cancer diagnosis, your doctor will determine the type of treatment that you need. You will have to see doctors of different specialties to find the best treatment for your condition. This will be determined by the type of cancer you have and whether it is stage II or advanced. If you have a family history of lung cancer, you’re at higher risk for developing the disease. If you have a family history of the disease, you can consult with different doctors to determine the best treatment for your case.
The doctor may recommend various treatment options. In some cases, chemotherapy may be the best option for you. Surgical treatment involves removing the tumor. Other treatments may include a combination of chemotherapy and radiation. During this procedure, your doctor will remove the cancerous cells in your lungs. A surgical procedure, however, is not always possible. A patient may need to undergo a biopsy to confirm a diagnosis. The biopsy will reveal if the cancer is staged or advanced.
