Heart disease can be prevented with a healthy lifestyle. Several lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and keeping a healthy diet, can help prevent the development of coronary artery disease. Once you have been diagnosed with the disease, you should not panic. You can still lead a healthy and active life. Be sure to follow the treatment plan recommended by your healthcare provider and ask any questions you may have. It is important to know that there is no cure for coronary artery diseases, but there are ways to manage the symptoms.
Getting a checkup is the first step. Your doctor will examine your blood vessels and take a detailed history to determine whether you have the condition. You may need to see a specialist for tests and treatments. You may need to undergo a few different procedures to make sure you have a correct diagnosis. Some of these procedures involve a procedure called angioplasty. This procedure involves inserting a balloon into the coronary artery and inflating it to open up the passageway. A stent is then inserted around the balloon and forms a scaffolding to hold the plaque in place.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of coronary artery disease, visit a doctor right away. You can check your arteries at any time, which is important as a blocked artery may obstruct blood flow to your heart. Even if you are asymptomatic, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. This will help you manage the condition before it becomes serious. A weakened heart is not only more likely to fail, but it can lead to death as well.
Getting a checkup is important as it can prevent a heart attack or other life-threatening heart condition. Depending on the severity of your CAD, it is important to see a doctor right away. A checkup is crucial for the treatment of coronary artery disease. You will need to take blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs. Taking care of the problem in its early stages can help you live a longer and healthier life.
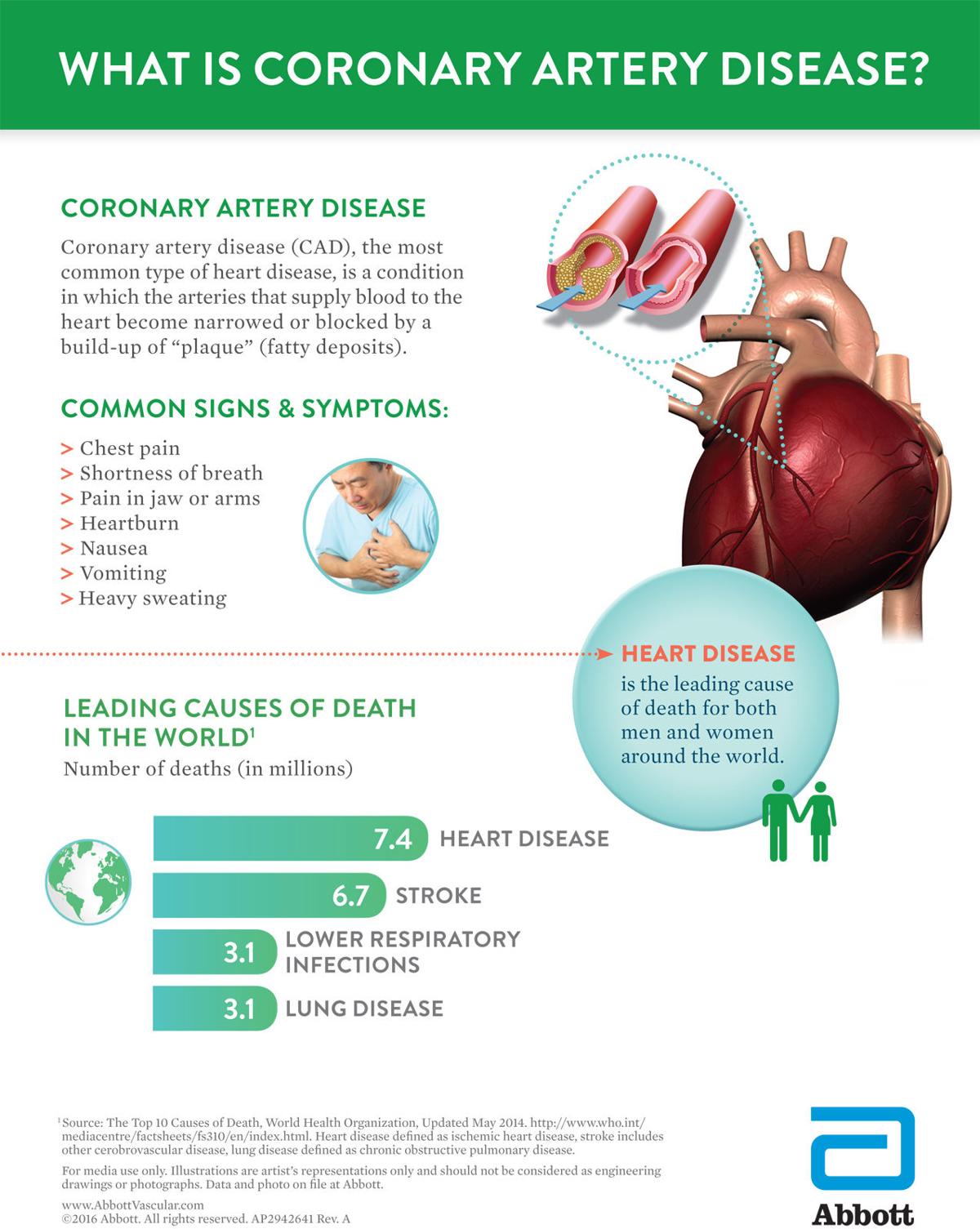
The first sign of coronary heart disease is chest pain. This is due to the fact that too many plaques accumulate in the arteries, preventing blood flow to the heart muscle. This can weaken the heart muscle, which can eventually lead to heart failure. If you feel chest pain, an examination may be required. If you experience any symptoms of coronary heart disease, you should contact your doctor immediately.
Most people experience a silent heart attack without warning. Fortunately, most patients show symptoms before an attack. The most common symptoms include chest pain and upper body pain. Other symptoms include jaw pain and stomach discomfort. Other signs are difficulty breathing and vomiting. Women are more likely to experience atypical symptoms than men, so listen to your body's signals and take action immediately. This may be a symptom of a more serious condition, so it is important to get tested.
The symptoms of a heart attack are the result of a blockage in a coronary artery. If the blockage is removed, the symptoms will disappear. A heart attack can also be caused by certain circumstances, including being overweight, not getting regular exercise, and smoking. Therefore, it is important to seek immediate medical attention if you notice any of these symptoms. There are several ways to diagnose a heart attack. The first thing you should do is visit a doctor and a health website igf2013.or.id. They can help you with various tests and procedures.
The most common symptom of a heart attack is chest pain. It is caused by too much plaque on the walls of the arteries. The blood vessels narrow and cannot carry blood to the rest of the body. It can weaken the heart muscle, causing a condition known as CAD. It can even lead to death. If you are experiencing chest pain, this is a sign of a serious heart condition.
While everyone is susceptible to coronary heart disease, the process can vary from person to person. For example, some people are at risk at a young age, while others are at risk in the early stages. In any case, the disease begins when streaks of fat begin to appear on the walls of blood vessels. As plaque grows, white blood cells begin to attack cholesterol and cause further inflammation. This causes the plaque to become larger and harder, which can trigger a heart attack.
