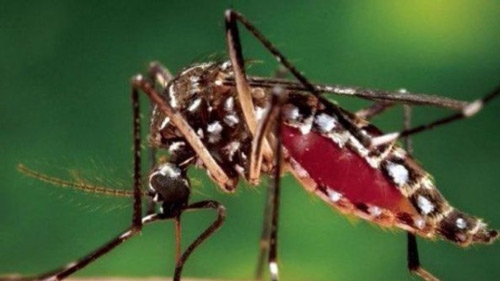
Many travelers are wondering, "What is chikungunya and why is it spreading?" The answer is simple: it is caused by a virus that causes inflammation of the joints and can cause acute fever. The symptoms can occur anywhere from two to twelve days after you have been infected. The first symptom is an onset of joint pain and fever, which may last a few days or last for weeks or months. It may also cause joint swelling and headache.
Other signs of chikungunya include muscle and joint pain, conjunctivitis, and fatigue. Some people also experience rashes and nausea. There is no known cure for chikungunya, but there is a variety of treatments to reduce the symptoms. In severe cases, the infection may lead to severe joint pain that can last months or even years. Because there is no vaccine or medicine to prevent the illness, treatment for chikungunya is based on treating the symptoms.
The only treatment for chikungunya is prevention. The condition is not contagious and most people recover on their own. The infection is not dangerous, but if it does not subside on its own, you may wish to see a doctor immediately. In the meantime, a doctor can give you ibuprofen or acetaminophen for joint pain. However, the disease can be more serious for certain groups of people. For instance, it is much more severe in newborns, people with a high blood pressure, and those with diabetes.
When it comes to chikungunya, the most definitive way to diagnose the condition is with blood tests. This is because if the symptoms are the same as those of dengue fever, the disease is almost impossible to distinguish. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember to rest and drink plenty of fluids. If you think you may have chikungunya, it is best to seek medical attention as soon as possible to avoid complications.

Although the symptoms of chikungunya are usually mild, the person may experience severe joint pain and high fever. The illness can last for months or even years, depending on the severity of the infection. Patients should wear long sleeves and apply mosquito repellant. If you have been exposed to the virus, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible and get advice on the site gs1.or.id. This will help ensure that you do not distribute it to your family members.
When it comes to symptoms, chikungunya is a virus that is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Symptoms of the virus include joint pain, fever, skin rash, and fatigue. This is a viral disease that can cause a rash and can be caused by a number of different conditions. Fortunately, the symptoms of the disease are usually mild and require a visit to the doctor only in case of a serious infection.
Symptoms of chikungunya include fever, rash, and muscle pain. Some people may experience severe joint pain while others experience mild symptoms. Some people may even experience conjunctivitis and a maculopapular rash. There is no specific treatment for the virus, but a person who develops the virus can be very susceptible to the disease. However, a doctor’s attention is needed to treat this condition in order to reduce the risk of death.
Although the disease is not contagious, it is important to take the necessary precautions to avoid it. If you are traveling to a tropical region, be sure to wear long sleeves and use an insect repellent with active ingredients. If you develop symptoms, see your doctor as soon as possible, as the disease can lead to life-threatening complications for your family. It is also important to protect those around you.
The main symptoms of chikungunya include fever, joint pain, and muscle aches. Often these symptoms last three to seven days and the symptoms can be severe. In severe cases, the disease can lead to a rash. Symptoms are often severe, and children under one year of age are particularly susceptible. If you suspect that you may have chikungunya, you should contact your doctor immediately. A doctor can confirm that you have the virus and test your blood for antibodies against the virus.
